Nova Scotia or New Scotland: When the ice age ended and the glacier retreated, nature took over, large and small animal species found their place and all kinds of plants took root. Indigenous peoples across the continent moved

The map shows North America, Canada in light color, the United States, Greenland and Iceland darker. Nova Scotia is colored red.
gradually into a previously unknown area, where life could be brought forward in harmony with plant and animal life. The Mi’kmaq tribe, which is a segment of the so-called Mi’kma’ki nation, traveled through the northeastern regions of North America that later became part of Canada. This ethnic group followed the seasons, chose a western settlement in the thick forest inland but moved to the seaside in the summer. The climate did not offer agriculture, but people engaged in animal and fishing activities. Indigenous peoples had their own government, a supreme council took power in the area where the nation had settled. The Supreme Council consisted of seven District Chiefs, but the land of the Mi’kmaq people was traditionally divided into seven, relatively independent districts. The district government enforced laws, allocated fishing rights, organized campaigns, and negotiated peace agreements.
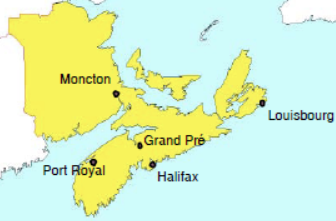
European Survey – Settlement: It was the Mi’maq people who ruled the lands and that the first European explorers met on their first voyages to North America. Europeans fished the east coasts of America, where the catch was salted and then shipped home. Almost no one lived on land but around 1520 a fish factory was set up on land and the Portuguese were the first inhabitants, they had a restaurant in Nova Scotia in the years 1551-1553 but probably longer because there is a source that mentions it in 1570. In 1578 were said about 350 ships and boats from Europe in St. Lawrence estuaries, which are the largest in the world. Most of them were fishing vessels, but a few had come there to explore the possibility of a fur trade. From the turn of the century in 1600, the French were quite active in this area and in 1605 a French colony called Acadia was created and made Port Royal their capital. The colony grew slowly, at first relying almost exclusively on explorers and merchants, but gradually families came west, and around 1863 such voyages from France are quite frequent. Indigenous peoples were unconcerned because by 1610, one of Mi’maq’s chiefs had converted to Catholicism and signed a treaty with the Catholic Church. It can be said that this oldest European colony in North America has received a very positive reviews because there was no war with the indigenous peoples. But the Acadians were not allowed to be at peace. The British invaded the French settlements from Boston in 1654 and seized all power, but with the Treaty of July 31, 1667, the French regained control. The Dutch were next and occupied Acadia in 1674, calling it New Holland, but failed to retain power there. During the last decades of the 17th century, the French settlements expanded somewhat when people moved from Port Royal and settled in Grand Pré, Chignecto, Cobequid and Pisiguit. Acadia’s independence came to an end because the British could not leave the colony alone, as they had endless disputes with France.


Here is a picture of the flag of Nova Scotia and in it you can see influences from the time of the Scots in the county in the 17th century. This can be clearly seen if you look at Williams’ coat of arms next to it.
New-Scotland: William Alexander of Scotland, well-educated and of noble lineage, was at the mercy of the British Crown and was appointed head of a large British territory, a baronial district called Nova Scotia in 1629. The area in question was where Nova Scotia and New Brunswick are today, but also included Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland as well as Maine in the United States. The capital of the Scottish colony was Port Royal, but the Scots did not succeed in seizing power in the West, and in 1632 they made a treaty with the French. Despite some domination, Scottish influence has led to one province of Canada bearing the name of Scotland. The French and British fought for control and Louisbourg was the center of that struggle. Gradually, the lines became clearer. In 1763 it became Cape Breton Island, and St. John’s Island (now Prince Edward Island) was part of Nova Scotia. St. John’s Island was an independent colony. By the middle of the 18th century, Halifax had become the capital of Nova Scotia, with British rule now covering almost the entire east coast of the continent. The American independence struggle led to the migration of thousands from the United States to Nova Scotia (Loyalists). It was in 1848 that Nova Scotia became the first British colony to gain autonomy, and in July 1867, together with New Brunswick and the Province of Canada (today Ontario and Quebec), a new nation-state, Canada, was established.
.
